Knee pain is a common ailment that can affect people of all ages. It can be caused by a variety of reasons, such as an injury, overuse during sports or exercise, a medical condition, or just natural wear and tear over time.
Whether it’s sharp, shooting pain in the knee or a dull, lasting ache, knee pain can be a nuisance and hamper your ability to take part in everyday activities and enjoy life. Fortunately, most knee pain is treatable and often responds well to at-home therapies.
This guide will provide insight into common causes of knee pain and the various ways to treat it.
Why Do My Knees Hurt? Common Causes of Knee Pain

A number of conditions and factors can make your knee hurt when you bend it or while it’s at rest. A doctor can perform a physical exam and may order imaging tests to confirm a knee-pain diagnosis. Common causes of pain in the knee include:
Knee Injuries
Sudden trauma can cause a knee ligament injury and damage tendons in the knee, cartilage, and bones that surround the knee, as well as those that make up the knee joint itself. Common knee injuries include:
ACL injury. An anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury is a tear in one of the four knee ligaments that connect the thigh bone to the shin bone in a normal knee. It’s a common injury in athletes who play soccer, basketball, or other sports that involve quick movements in different directions.
Bursitis. Inflammation of the bursae — the small fluid-filled sacs that protect the outside of the knee joint — can result from overuse, repeated pressure on the knee, strenuous activity, or a blow to the knee.
Torn meniscus. A sudden twist of the knee while bearing weight on it can lead to a tear of the meniscus — the cartilage that acts as a cushion between the thigh and shin bones. This is a common injury among athletes who play contact sports.
Dislocated knee cap. Dislocation can cause kneecap pain. When the bone that covers the knee (called the patella) slips out of place, dislocation occurs. This can happen after a sudden change in direction when your leg is firmly in place.
Fracture. Falls or car accidents can lead to a knee fracture, or a break.
Strain or sprain. Unnatural twisting may lead to mild damage to the knee ligaments, causing a strain or sprain.
Overuse

Repetitive activities can lead to strain on the knee, which can cause pain. Common examples include:
Runner’s knee. Dull pain under or around the kneecap is often referred to as runner’s knee. As the name implies, running is a common cause of this pain, but any activity that causes repeated stress to the knee, including walking, cycling, jumping, skiing, or playing sports, can lead to the condition.
Tendonitis. Inflammation of the knee tendons (the pieces of connective tissue between muscles and bones) can result from repetitive motions that put excess strain on the knee, such as participating in sports or physical labor.
Arthritis
Arthritis — or the pain, swelling, and stiffness of one or more joints — is a common cause of knee pain. Types of arthritis that affect the knees include:
Osteoarthritis. This is the most common type of arthritis. It is characterized by the breakdown of the cartilage in the knee due to wear and tear with age.
Rheumatoid arthritis. The most debilitating form of arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. This means the immune system attacks healthy cells in the body by mistake causing painful swelling and inflammation. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect any joint in the body, including the knees.
Lyme arthritis. The spirochetes that cause Lyme disease can cause arthritis in the knees and other joints. Most often, this starts out as intermittent pain that moves from joint to joint gradually becomes permanent if not treated. Some Lyme sufferers start with left knee pain, right knee pain, or pain in the knee and arm that vanishes and reappears and spreads to other joints.
How Can You Treat Arthritis with Cold Therapy? Read our guide to find out
Surgery
Following knee surgery, some pain, tenderness, and swelling is to be expected. For people who have undergone knee replacement surgery, a degree of pain is normal for several months after the procedure.
Your healthcare provider will work with you on ways to manage the pain, including medication and physical therapy.
Common Symptoms of Knee Injuries
Severity and type of knee pain associated with injuries can vary depending on its cause. Some common symptoms of knee injuries include:
- Pain, which can be described as sharp and stabbing or dull and achy. Knee pain when walking, knee pain when bending, pain behind the knee (back of the knee pain) and pain in the side of the knee can be signs of an injury.
- Knee swelling and knee inflammation
- Stiffness
- Redness and warmth to the touch on and around the knee
- Instability or a weak knee, giving way when you bear weight your knee
- Inability to fully flex or extend the knee
How to Treat Knee Pain

There are a number of options to treat knee pain. It can often be managed with at-home remedies, medication, and physical therapy. In some instances, surgery may be necessary.
See your doctor about knee pain caused by an accident or injury.
At-Home Treatments for Knee Pain
Many forms of knee pain can be treated at home. If your symptoms aren’t severe and they started recently, try these common strategies to ease knee pain:
Rest. Reduce repetitive strain on your knee by avoiding movement as much as possible and keeping weight off it. For minor injuries, a day or two of rest may be sufficient to alleviate knee pain, while more serious damage may require that you keep weight off your knee longer.

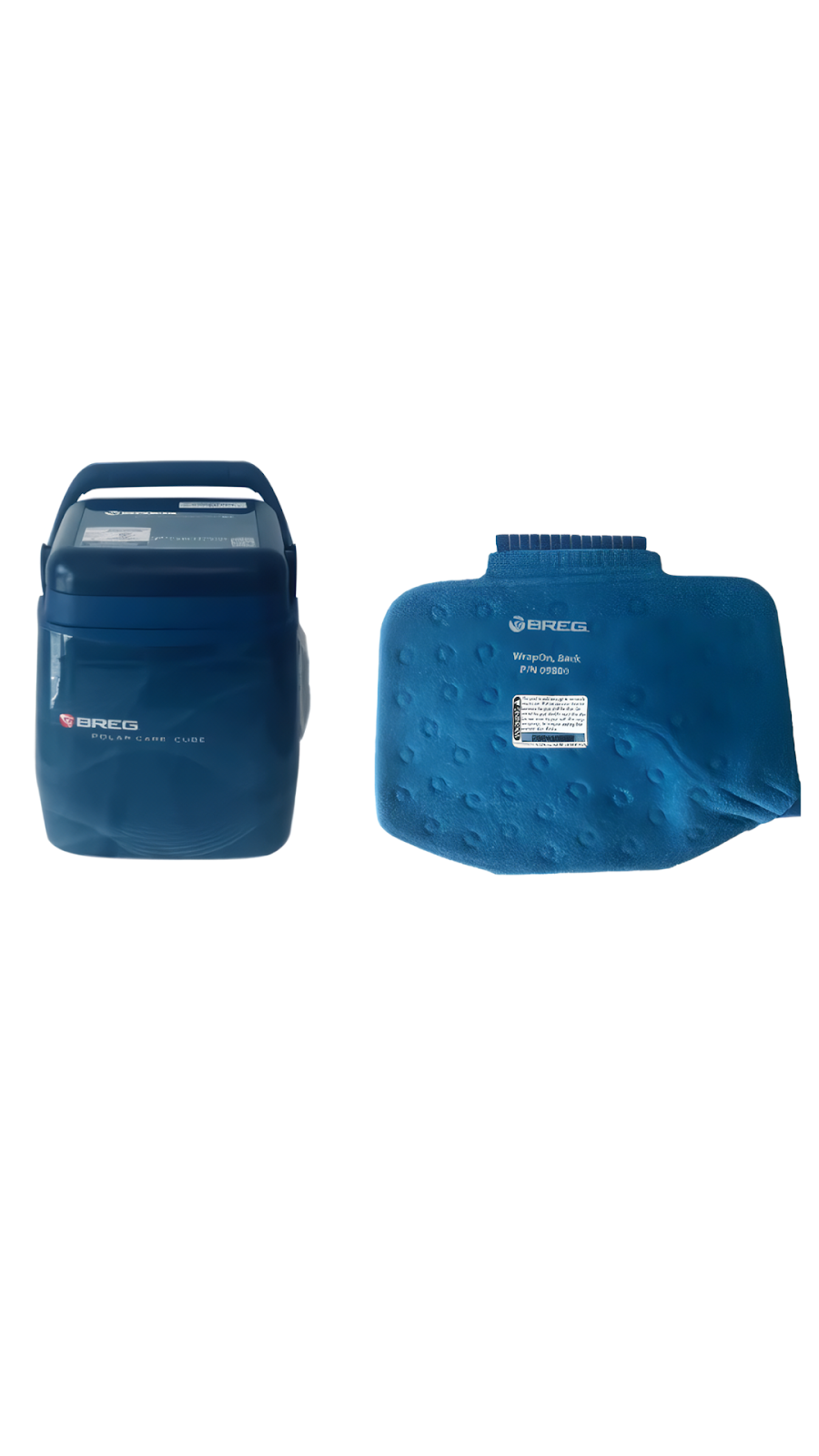
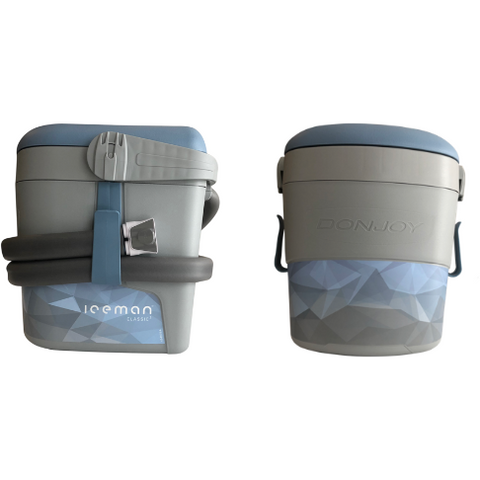
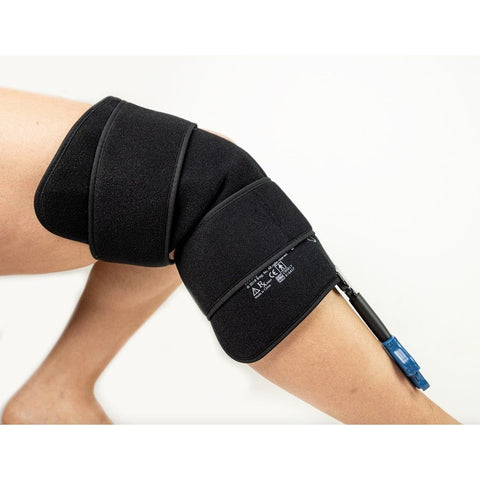
Cold therapy. Applying ice or cold temperatures to the affected area can numb pain and help reduce swelling. Try using a bag of peas or an ice pack wrapped in a thin towel. Apply for 20 minutes several times a day. Cold therapy machines are mainly found in hospitals and physical therapy clinics but are also available for home use. These cold therapy units for knees circulate cold water through a knee pad or wrap applied to the area. Breg cold therapy products offer targeted treatment for knee pain with knee-specific padding. For a full list of the best at-home cryotherapy units, explore the Best Cold Therapy Machines for Knee Pain guide.
Heat therapy. You might also find relief from knee pain (and knee muscle pain) by alternating cold therapy with heat therapy. Hot packs, a heating pad, or a hot water bottle may be used to apply heat to the affected area.
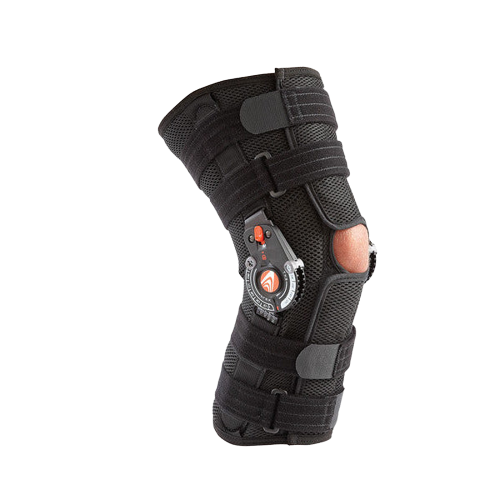
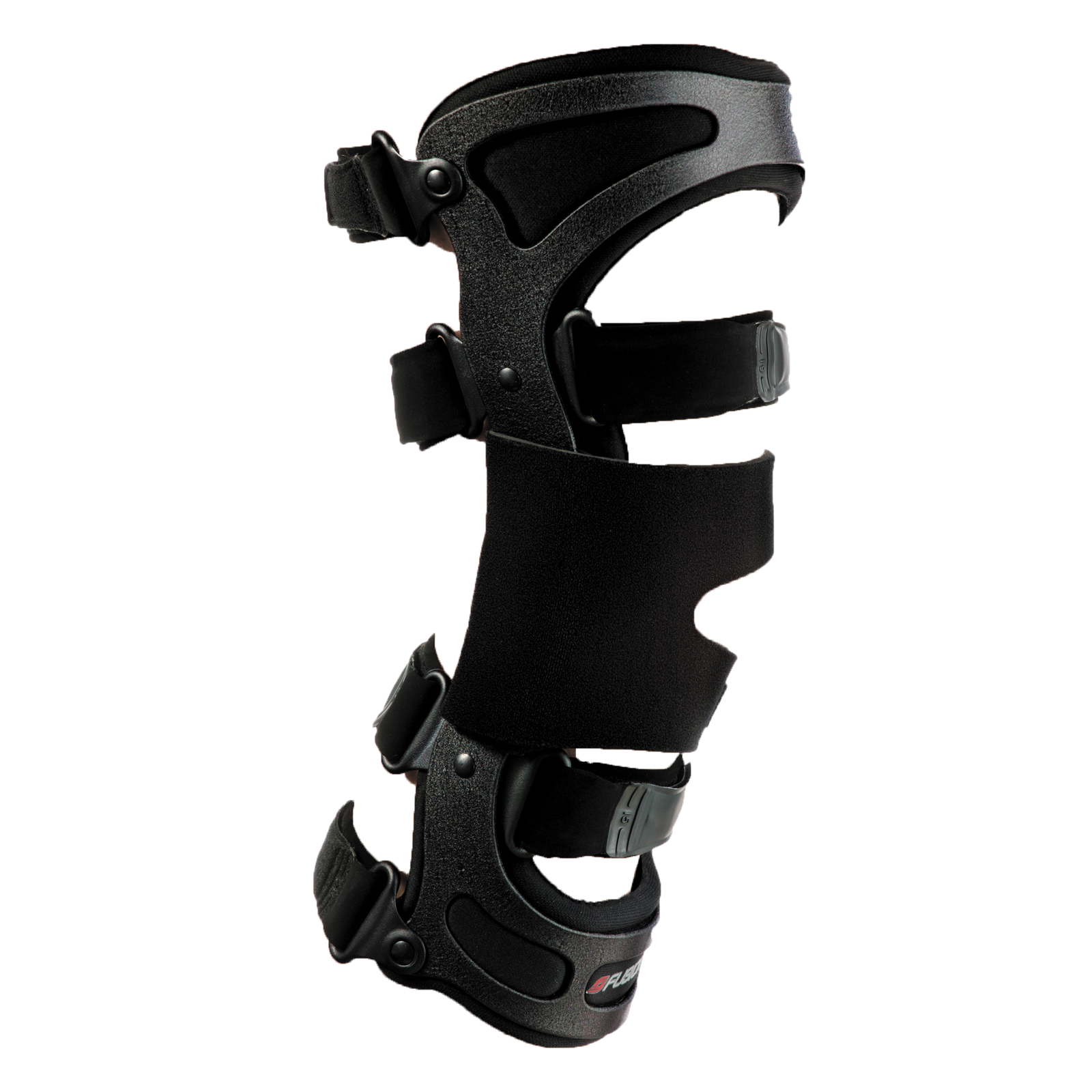
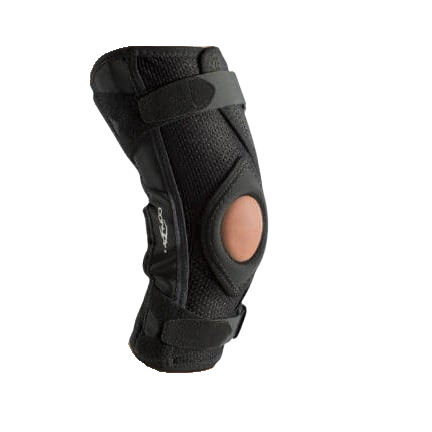
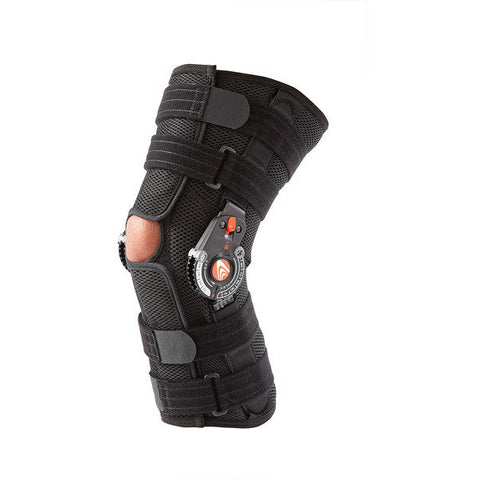
Compression. Compressing the knee can help prevent fluid build up, keeping swelling under control. It can also help maintain alignment and stability. Choose a brace or compression bandage that’s breathable and tight enough to provide support without cutting off blood circulation. Donjoy, Breg, and ProCare, are some brands that offer excellent support for painful knees. If you’re not sure which device will suit your needs, check out these guides on the Best Compression Sleeves and Best Hinged Knee Braces.
Elevation. Keeping your knee propped up as much as possible will help reduce any swelling.
Medications and Injections
Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers to ease pain and swelling associated with knee injuries. If you’re suffering from osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, you may need medication to treat those conditions.
In some instances, your doctor may recommend injecting medication directly into your joints to temporarily relieve pain and swelling. Examples include corticosteroids and hyaluronic acid, a thick fluid that resembles the fluid which naturally lubricates joints.
Physical Therapy
Strengthening your knee muscles with movements and exercises can be an effective way to treat knee pain. A physical therapist can work with you on different types of exercises depending on the injury or condition that’s causing your pain.
Exercises that improve flexibility and balance can also help improve knee pain.
Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle changes can help prevent and ease knee pain. These include:
- Remembering to warm up before exercise and cool down after. Stretching your quadriceps (the muscles in the front of the thigh) and hamstrings (those in the back of the thigh) is particularly important when it comes to a sore knee.
- Losing weight if you are overweight
- Avoiding running on cement or pavement, as well as running down hills. The ideal surface to run on is smooth and soft, such as a track. It’s best to walk downhill.
- If running causes knee pain, try other forms of exercise, such as cycling or swimming.
- If you have flat feet, talk to your doctor about orthotics, or special shoe or heel inserts.
- Assure running shoes are appropriate and fit well.
Surgery
If you have severe knee pain that interferes with daily activities and has not responded to other therapies, your doctor may recommend surgery. You may also need surgery if the knee has structural damage.
Your doctor will discuss the pros and cons of knee surgery with you. Types of knee surgery include:
Arthroscopic surgery. In this minimally-invasive procedure, a healthcare provider uses narrow tools and a small fiber-optic camera inserted through incisions around the knee to repair joint damage. This type of surgery can be used to treat torn ligaments, damaged cartilage, and loose bodies that need to be removed from the knee joint.
Knee replacement surgery. Replacement surgery can be done on part of the knee or the whole joint. Partial knee replacement surgery entails replacing only the most damaged portions of the knee with artificial parts made of plastic and metal. During total knee replacement surgery, a surgeon removes damaged bone and cartilage from the thigh bone, shinbone, and kneecap, replacing them with an artificial joint.
Osteotomy. This procedure may be done to treat arthritis pain in the knee. The surgery involves cutting and removing bones in the thigh and the shin to better align the knee.
Should I Get Knee Surgery?
Surgery is a big decision and not one that should be taken lightly. For most types of knee surgery, it is not necessary to have the procedure done right away.
Surgery is typically considered when other types of therapy to treat knee pain fail. Your doctor will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of knee surgery versus nonsurgical rehabilitation.
Before making the final call on surgery, it’s wise to try bracing, cold therapy, strengthening exercises, and other recovery methods to see if they ease your knee pain..
How to Recover from Knee Surgery
How you will recover from knee surgery depends on the type of procedure you have. A knee arthroscopy is minimally invasive and much less involved than a knee replacement surgery, with a shorter recovery time.
However, everyone responds to surgery differently. Even with less-invasive procedures, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about when you can return to everyday activities like walking without assistance and driving.
Hospital Stay
After knee replacement surgery, you’ll typically remain in the hospital for one to four days. Before you can be discharged you will need to demonstrate that you can do basic activities on your own, such as getting in and out of bed, eating, drinking, using the bathroom, and walking with an assistive device like a cane, crutches, or a walker.
Medications
Your doctor may prescribe you a number of medications, including opioid and non-opioid pain relievers, blood thinners, stool softeners, and anti-nausea medications. Take all medications as directed.
Physical Therapy
Your doctor or physical therapist will work with you on movements and strengthening exercises that will help you recover from knee replacement surgery. You should expect to do these exercises for at least two months.
Elevating your leg can help to prevent swelling, as can cold therapy and compression.
Your doctor will discuss when you can expect to return to your normal activities.
Treating Knee Pain - The Bottom Line
Knee pain is a common ailment and there are a number of knee-pain causes from injury to overuse to certain health conditions.
When it comes to treating knee pain, there are a variety of options available. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help temporarily ease discomfort, while exercises focused on balance, flexibility, and strengthening the muscles around the knee can help lessen and even relieve pain.
Home remedies to treat knee pain can also be extremely beneficial. Rest, compression, elevation, and ice are tried and true methods that work to relieve joint pain. Consider cold therapy machines and knee braces from Orthobracing to help fix your knee troubles.
Read on:
Best Cold Therapy Machines for Faster Recovery
At Home Cryotherapy: How to Do It & What to Know
Top Benefits of Cold Compression
Best Neck Stretchers for Pain Relief
Best Back Braces for Quicker Recovery
Best Shoulder Braces for Pain Relief
Best Shoulder Compression Sleeves: What to Look For
Game Ready Ice Machine: Everything to Know (and Some Cheaper Alternatives)